有人對(duì)osal處理消息的機(jī)制及如果有數(shù)據(jù)包接收,協(xié)議棧到底是怎么來處理得到所需要的數(shù)據(jù)的有點(diǎn)不清楚,以下我簡(jiǎn)單的按照我的理解寫一下。
其實(shí)只要觸發(fā)SYS_EVENT_MSG事件,首先都會(huì)有這樣一個(gè)語(yǔ)句: MSGpkt = (afIncomingMSGPacket_t *)osal_msg_receive( SampleApp_TaskID ); 讓我們一步一步看下函數(shù)的意思,首先是osal_msg_receive()這個(gè)函數(shù),來看一下原型: @fn osal_msg_receive
*
* @brief
*
* This function is called by a task to retrieve a received command
* message. The calling task must deallocate the message buffer after
* processing the message using the osal_msg_deallocate() call.
*函數(shù)描述: 該函數(shù)通過一個(gè)任務(wù)調(diào)用來檢索收到的命令信息。調(diào)用的任務(wù)必須在利用osal_msg_deallocate()函數(shù)處理信息之后必須釋放消息占用的內(nèi)存。
* @param byte task_id - receiving tasks ID
*收到的任務(wù)ID
* @return *byte - message information or NULL if no message
*消息信息或者空指針
byte *osal_msg_receive( byte task_id )
{
osal_msg_hdr_t *listHdr;
osal_msg_hdr_t *prevHdr=0;
halIntState_t intState; // Hold off interrupts
HAL_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState); 這個(gè)主要用于暫緩中斷 // Point to the top of the queue
listHdr = osal_qHead; 指向消息隊(duì)列的頭部 // Look through the queue for a message that belongs to the asking task 在隊(duì)列中查找屬于該任務(wù)的消息。
while ( listHdr != NULL )
{
if ( (listHdr - 1)->dest_id == task_id )
{
break;
}
prevHdr = listHdr;
listHdr = OSAL_MSG_NEXT( listHdr );
} // Did we find a message? 是否找到消息?
if ( listHdr == NULL )
{
// Release interrupts 釋放中斷
HAL_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState);
return NULL;
} // Take out of the link list 從鏈接鏈表中拿出。
osal_msg_extract( &osal_qHead, listHdr, prevHdr ); // Release interrupts
HAL_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState); return ( (byte*) listHdr );
} 這個(gè)函數(shù)看來主要是提取屬于該任務(wù)的消息,osal在后臺(tái)維護(hù)一個(gè)消息隊(duì)列,對(duì)應(yīng)的任務(wù)可以在該消息隊(duì)列中提取到屬于自己的消息,從而判斷是哪個(gè)時(shí)間需要處理,但這又有一個(gè)問題,到底o(hù)sal怎么把消息送到osal的消息隊(duì)列中去呢,看來還有一些問題沒搞清楚,沒事,咱在繼續(xù)研究,讓我們?cè)诔绦蛑泻煤谜艺遥@就涉及到osal運(yùn)行方式了,我們好好看看,一定要弄明白: 我們都知道在開發(fā)自己的應(yīng)用程序時(shí),對(duì)于我們開發(fā)者來說,一個(gè)任務(wù)包括最主要的兩個(gè)部分:首先要做的是做的是寫任務(wù)初始化函數(shù),然后是相應(yīng)的事件處理函數(shù)。當(dāng)然,最后一步是將自己編寫的任務(wù)添加到osal任務(wù)隊(duì)列中去,這個(gè)主要由osalAddTasks()函數(shù)來完成。 而對(duì)于整個(gè)osal運(yùn)行來說,主要的過程如下: 首先主要是進(jìn)行一系列的初始化,然后就是進(jìn)入一個(gè)死循環(huán)函數(shù)osal_start_system() ZSEG int main( void )
{
// Turn off interrupts
osal_int_disable( INTS_ALL );
// Make sure supply voltage is high enough to run
zmain_vdd_check(); // Initialize stack memory
zmain_ram_init(); // Initialize board I/O
InitBoard( OB_COLD ); // Initialze HAL drivers
HalDriverInit(); // Initialize NV System
osal_nv_init( NULL ); // Determine the extended address
zmain_ext_addr(); // Initialize basic NV items
zgInit(); // Initialize the MAC
ZMacInit(); #ifndef NONWK
// Since the AF isn't a task, call it's initialization routine
afInit();
#endif // Initialize the operating system
osal_init_system(); // Allow interrupts
osal_int_enable( INTS_ALL ); // Final board initialization
InitBoard( OB_READY ); // Display information about this device
zmain_dev_info();
#ifdef LCD_SUPPORTED
zmain_lcd_init();
#endif osal_start_system(); // No Return from here
} // main() osal_start_system()這個(gè)函數(shù)的原型如下:其主要功能是執(zhí)行任務(wù)隊(duì)列中的任務(wù)。主要是通過不斷循環(huán)來實(shí)現(xiàn)。 void osal_start_system( void )
{
uint16 events;
uint16 retEvents;
byte activity;
halIntState_t intState; // Forever Loop
#if !defined ( ZBIT )
for(;;)
#endif
{
Hal_ProcessPoll();// activity = false; activeTask = osalNextActiveTask();
if ( activeTask )
{ 如果有任務(wù)的話就暫緩中斷。
HAL_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState);
events = activeTask->events;//進(jìn)入事件
// Clear the Events for this task
activeTask->events = 0;//對(duì)應(yīng)事件清0
HAL_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState); 開放總斷。 if ( events != 0 )
{
// Call the task to process the event(s)
if ( activeTask->pfnEventProcessor )// 調(diào)用相應(yīng)的任務(wù)事件處理函數(shù)
{
retEvents = (activeTask->pfnEventProcessor)( activeTask->taskID, events ); // Add back unprocessed events to the current task
HAL_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState);
activeTask->events |= retEvents;
HAL_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState); activity = true;
}
}
} // Complete pass through all task events with no activity?
if ( activity == false )//沒有相應(yīng)的任務(wù)需要處理后就進(jìn)入休眠模式。
{
#if defined( POWER_SAVING )
// Put the processor/system into sleep
osal_pwrmgr_powerconserve();//進(jìn)入休眠
#endif
}
} 整個(gè)流程下來,你可能并不知道任務(wù)里的事件是怎么觸發(fā)的,消息是怎么進(jìn)行傳遞的,所以得繼續(xù)往下看(有點(diǎn)亂是吧,沒辦法,哥們,沒經(jīng)過整理的東西往往是這么無(wú)力,O(∩_∩)O哈哈~)來,繼續(xù): 這個(gè)函數(shù)里面一個(gè)關(guān)鍵函數(shù)是Hal_ProcessPoll(),不要小看這個(gè)函數(shù),這個(gè)函數(shù)為系統(tǒng)設(shè)置了一個(gè)"心跳",稱之為心跳的原因主要是因?yàn)檫@個(gè)設(shè)置了一個(gè)定時(shí)器作為osal運(yùn)行的時(shí)鐘,現(xiàn)在的關(guān)鍵是搞清楚這個(gè)時(shí)鐘在哪設(shè)置,怎樣引導(dǎo)osal工作(好像扯得遠(yuǎn)了,沒事,把這些先慢慢搞清楚,然后就知道消息的傳送過程)這個(gè)函數(shù)調(diào)用的是這個(gè)函數(shù) HalTimerTick(),這個(gè)函數(shù)原型如下: void HalTimerTick (void)
{
if (!halTimerRecord[HW_TIMER_1].intEnable)
{
halProcessTimer1 ();
} if (!halTimerRecord[HW_TIMER_3].intEnable)
{
halProcessTimer3 ();
} if (!halTimerRecord[HW_TIMER_4].intEnable)
{
halProcessTimer4 ();
}
} 媽的,出了點(diǎn)問題,我不知道這些計(jì)時(shí)器的配置函數(shù)在哪,到底是哪個(gè)定時(shí)器作為osal運(yùn)行的時(shí)鐘呢,halTimerRecord[HW_TIMER_1].intEnable到底是在哪配置的我沒找到相應(yīng)的函數(shù),沒事,等等,繼續(xù)找。。。。 按照我的感覺如果在osal任務(wù)初始化函數(shù)中(初始化我會(huì)拿另一節(jié)來講,這節(jié)就只講講這個(gè))肯定可以找到一些端倪,于是按照思路找下去,有了一個(gè)不錯(cuò)的發(fā)現(xiàn):這個(gè)是板級(jí)初始化函數(shù),我們來找, void InitBoard( byte level )
{
if ( level == OB_COLD )
{
// Initialize HAL
HAL_BOARD_INIT();
// Interrupts off
osal_int_disable( INTS_ALL );
// Turn all LEDs off
HalLedSet( HAL_LED_ALL, HAL_LED_MODE_OFF );
// Check for Brown-Out reset
ChkReset();
OnboardTimerIntEnable = FALSE;
HalTimerConfig (OSAL_TIMER, // 8bit timer2
HAL_TIMER_MODE_CTC, // Clear Timer on Compare
HAL_TIMER_CHANNEL_SINGLE, // Channel 1 - default
HAL_TIMER_CH_MODE_OUTPUT_COMPARE, // Output Compare mode
OnboardTimerIntEnable, // Use interrupt
Onboard_TimerCallBack); // Channel Mode } 最主要的是這個(gè)函數(shù) HalTimerConfig()設(shè)置了時(shí)鐘。
else // !OB_COLD
{
#ifdef ZTOOL_PORT
MT_IndReset();
#endif
OnboardKeyIntEnable = HAL_KEY_INTERRUPT_DISABLE;
HalKeyConfig( OnboardKeyIntEnable, OnBoard_KeyCallback);
} 來看下HalTimerConfig()的原型: uint8 HalTimerConfig (uint8 timerId, uint8 opMode, uint8 channel, uint8 channelMode,
bool intEnable, halTimerCBack_t cBack)
{
uint8 hwtimerid; hwtimerid = halTimerRemap (timerId); if ((opMode & HAL_TIMER_MODE_MASK) && (timerId < HAL_TIMER_MAX) &&
(channelMode & HAL_TIMER_CHANNEL_MASK) && (channel & HAL_TIMER_CHANNEL_MASK))
{
halTimerRecord[hwtimerid].configured = TRUE;
halTimerRecord[hwtimerid].opMode = opMode;
halTimerRecord[hwtimerid].channel = channel;
halTimerRecord[hwtimerid].channelMode = channelMode;
halTimerRecord[hwtimerid].intEnable = intEnable;
halTimerRecord[hwtimerid].callBackFunc = cBack;//設(shè)置回調(diào)函數(shù)的指針。
}
else
{
return HAL_TIMER_PARAMS_ERROR;
}
return HAL_TIMER_OK;
} 層層調(diào)用我最后找到了這個(gè)函數(shù)(層層調(diào)用的我就不寫出來了,只寫最主要的) void osal_update_timers( void )
{
osalTimerUpdate( tmr_decr_time );//tmr_decr_time在void osalTimerInit( void )賦值,為: tmr_decr_time = TIMER_DECR_TIME;define TIMER_DECR_TIME 1 // 1ms - has to be matched with TC_OCC 即是一毫秒即是每隔一毫秒更新一次定時(shí)器。但是有一個(gè)問題,我在例子中看到這個(gè)定時(shí)器沒有被打開。 } osalTimerUpdate( tmr_decr_time )原型:
*********************************************************************
* @fn osalTimerUpdate
*
* @brief Update the timer structures for a timer tick.
*更新定時(shí)器的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu) * @param none
*
* @return none
*********************************************************************/
static void osalTimerUpdate( uint16 updateTime )//這個(gè)函數(shù)真有點(diǎn)讓我有點(diǎn)摸不著頭腦,不知道為啥多出來一個(gè)定時(shí)器鏈表。
{
halIntState_t intState;
osalTimerRec_t *srchTimer;
osalTimerRec_t *prevTimer;
osalTimerRec_t *saveTimer; HAL_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION( intState ); // Hold off interrupts. // Update the system time
osal_systemClock += updateTime; // Look for open timer slot
if ( timerHead != NULL )
{
// Add it to the end of the timer list
srchTimer = timerHead;
prevTimer = (void *)NULL; // Look for open timer slot
while ( srchTimer )
{
// Decrease the correct amount of time
if (srchTimer->timeout <= updateTime)
srchTimer->timeout = 0;
else
srchTimer->timeout = srchTimer->timeout - updateTime; // When timeout, execute the task
if ( srchTimer->timeout == 0 )
{
osal_set_event( srchTimer->task_id, srchTimer->event_flag );//這個(gè)函數(shù)又是關(guān)鍵。 // Take out of list
if ( prevTimer == NULL )
timerHead = srchTimer->next;
else
prevTimer->next = srchTimer->next; // Next
saveTimer = srchTimer->next; // Free memory
osal_mem_free( srchTimer ); srchTimer = saveTimer;
}
else
{
// Get next
prevTimer = srchTimer;
srchTimer = srchTimer->next;
}
} #ifdef POWER_SAVING
osal_retune_timers();這個(gè)函數(shù)以后再說。
#endif
} HAL_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION( intState ); // Re-enable interrupts.
} 還是先上一個(gè)圖說明定時(shí)器數(shù)據(jù)鏈表吧,該圖來自?shī)W特曼的筆記: 其實(shí)就是一個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu),沒啥復(fù)雜的,不要想復(fù)雜了, typedef struct
{
void *next;
UINT16 timeout;
UINT16 event_flag;
byte task_id;
} osalTimerRec_t;。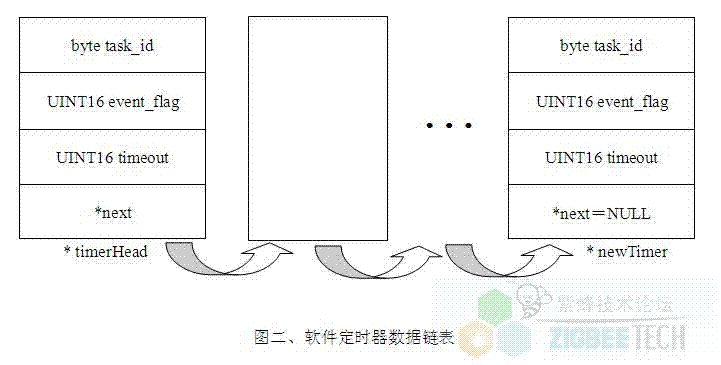
有點(diǎn)暈,先不管上面的了,我不知道上面這個(gè)鏈表是怎么更新的,即是上述的鏈表的值是怎么賦值的,為什么要搞個(gè)這樣的表出來?(媽的,為了搞清楚開頭的那玩意跑到現(xiàn)在這么遠(yuǎn)的地方了,越說越遠(yuǎn),沒辦法了,打破砂鍋問到底吧)先把這個(gè)高清楚之后在來看上面函數(shù)的具體作用,我看了奧特曼寫的一些東西,感覺有些不是很對(duì),但是他說的一個(gè)函數(shù)引起了我的注意,這就是
byte osal_start_timerEx( byte taskID, UINT16 event_id, UINT16 timeout_value )
{
halIntState_t intState;
osalTimerRec_t *newTimer;
HAL_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION( intState ); // Hold off interrupts. // Add timer
newTimer = osalAddTimer( taskID, event_id, timeout_value );
添加一個(gè)新的任務(wù)到定時(shí)器鏈表中。 if ( newTimer )
{
#ifdef POWER_SAVING
// Update timer registers
osal_retune_timers();
(void)timerActive;
#endif
// Does the timer need to be started? //現(xiàn)在如果定時(shí)器沒有啟動(dòng),那么啟動(dòng)定時(shí)器
if ( timerActive == FALSE )
{
osal_timer_activate( TRUE );//媽的,原來是在這里啟動(dòng)的,難怪在osal初始化中可以開始不啟動(dòng)。搞的我心里惴惴不安,還以為自己看錯(cuò)了,
}
} HAL_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION( intState ); // Re-enable interrupts. return ( (newTimer != NULL) ? ZSUCCESS : NO_TIMER_AVAIL );
} 搞清楚了這個(gè)函數(shù),看來這個(gè)函數(shù)主要的任務(wù)是將任務(wù)的一個(gè)對(duì)應(yīng)事件送到上述的定時(shí)器鏈表中,那上面那個(gè)函數(shù)怎么執(zhí)行呢,問題又來了,什么樣的情況下才去運(yùn)行osalTimerUpdate()這個(gè)函數(shù)呢,在初始化的過程中運(yùn)行了一次,但是,后來又是怎么運(yùn)行的呢,如果是靠定時(shí)器溢出來運(yùn)行的,那么這個(gè)機(jī)制又是怎樣的呢? 繼續(xù)看程序,繼續(xù)思考,別急。。。。。 查了有關(guān)資料,如果定時(shí)器溢出會(huì)調(diào)用這個(gè)函數(shù)halTimerSendCallBack(),看一下這個(gè)函數(shù)的原型, void halTimerSendCallBack (uint8 timerId, uint8 channel, uint8 channelMode)
{
uint8 hwtimerid; hwtimerid = halTimerRemap (timerId); if (halTimerRecord[hwtimerid].callBackFunc)
(halTimerRecord[hwtimerid].callBackFunc) (timerId, channel, channelMode);
}
即如果系統(tǒng)定時(shí)器溢出后將調(diào)用這個(gè)函數(shù)(調(diào)用機(jī)制等下再來看)并找出對(duì)應(yīng)的定時(shí)器回調(diào)函數(shù),系統(tǒng)定時(shí)器的回調(diào)函數(shù)是這個(gè)void Onboard_TimerCallBack ( uint8 timerId, uint8 channel, uint8 channelMode)
{ if ((timerId == OSAL_TIMER) && (channelMode == HAL_TIMER_CH_MODE_OUTPUT_COMPARE))
{
osal_update_timers();
}
} 這樣就知道了如果定時(shí)器每溢出一次將會(huì)調(diào)用這個(gè)osal_update_timers();函數(shù)一次,現(xiàn)在我們?cè)倩貋砜纯吹降姿麐尩倪@個(gè)函數(shù)是干嘛用的:。。。。。。。。 osalTimerUpdate( tmr_decr_time )原型:
*********************************************************************
* @fn osalTimerUpdate
*
* @brief Update the timer structures for a timer tick.
*更新定時(shí)器的數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu) * @param none
*
* @return none
*********************************************************************/
static void osalTimerUpdate( uint16 updateTime ) {
halIntState_t intState;
osalTimerRec_t *srchTimer;
osalTimerRec_t *prevTimer;
osalTimerRec_t *saveTimer;//這些是鏈表的相應(yīng)指針,不要怕,知道嗎,都學(xué)過了,呵呵 HAL_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION( intState ); // Hold off interrupts. // Update the system time
osal_systemClock += updateTime;//更新系統(tǒng)時(shí)間,這個(gè)osal_systemClock 是一個(gè)非常大的數(shù),static uint32 osal_systemClock; // Look for open timer slot
if ( timerHead != NULL )
{
// Add it to the end of the timer list
srchTimer = timerHead;
prevTimer = (void *)NULL; // Look for open timer slot
while ( srchTimer )
{
// Decrease the correct amount of time
if (srchTimer->timeout <= updateTime)
srchTimer->timeout = 0;
else
srchTimer->timeout = srchTimer->timeout - updateTime; // When timeout, execute the task
if ( srchTimer->timeout == 0 )
{
osal_set_event( srchTimer->task_id, srchTimer->event_flag );//這個(gè)函數(shù)又是關(guān)鍵。 // Take out of list
if ( prevTimer == NULL )
timerHead = srchTimer->next;
else
prevTimer->next = srchTimer->next; // Next
saveTimer = srchTimer->next; // Free memory
osal_mem_free( srchTimer ); srchTimer = saveTimer;
}
else
{
// Get next
prevTimer = srchTimer;
srchTimer = srchTimer->next;
}
} #ifdef POWER_SAVING
osal_retune_timers();這個(gè)函數(shù)以后再說。
#endif
} HAL_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION( intState ); // Re-enable interrupts.
} 這下應(yīng)該看懂了吧,主要是在timeout的時(shí)間后執(zhí)行 osal_set_event( srchTimer->task_id, srchTimer->event_flag );好的先,把大體流程總結(jié)一下在來看,如果假設(shè)利用osal_start_timerEx()函數(shù)設(shè)置了一個(gè)事件,并將其加入到定時(shí)器鏈表中,這時(shí)候定時(shí)器啟動(dòng),并且如果溢出的時(shí)候就會(huì)調(diào)用osalTimerUpdate()函數(shù),在每次執(zhí)行后都會(huì)檢查時(shí)間對(duì)應(yīng)timeout是否等于0,如果等于零的時(shí)候就會(huì)調(diào)用這個(gè)函數(shù)osal_set_event( srchTimer->task_id, srchTimer->event_flag),現(xiàn)在我們來仔細(xì)看一下這個(gè)函數(shù),
byte osal_set_event( byte task_id, UINT16 event_flag )
{
osalTaskRec_t *srchTask;
halIntState_t intState;
srchTask = osalFindTask( task_id );//找到這個(gè)任務(wù)
if ( srchTask ) {
// Hold off interrupts
HAL_ENTER_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState);
// Stuff the event bit(s)
srchTask->events |= event_flag;//設(shè)定相應(yīng)事件的標(biāo)志。 ************************************** 注:這里的events標(biāo)志可以設(shè)定為一個(gè)非零值,而這個(gè)非零值就是對(duì)應(yīng)的事件,在執(zhí)行的時(shí)候就是根據(jù)相應(yīng)的值來執(zhí)行相應(yīng)的事件。 **************************************
// Release interrupts
HAL_EXIT_CRITICAL_SECTION(intState);
}
else
return ( INVALID_TASK ); return ( ZSUCCESS );
} 這下知道了這個(gè)函數(shù)主要是置位相應(yīng)的事件,然后傳給系統(tǒng)的處理,系統(tǒng)處理這個(gè)主要是經(jīng)過輪詢 主要靠這個(gè)函數(shù)實(shí)現(xiàn): osalTaskRec_t *osalNextActiveTask( void )
{
osalTaskRec_t *srchTask; // Start at the beginning
srchTask = tasksHead; // When found or not
while ( srchTask ) {
if (srchTask->events) {
// task is highest priority that is ready
return srchTask;
}
srchTask = srchTask->next;
}
return NULL;
} 它返回一個(gè)指向typedef struct osalTaskRec
{
struct osalTaskRec *next;
pTaskInitFn pfnInit;
pTaskEventHandlerFn pfnEventProcessor;
byte taskID;
byte taskPriority;
uint16 events; } osalTaskRec_t; 的指針。
然后將任務(wù)交給retEvents = (activeTask->pfnEventProcessor)( activeTask->taskID, events );這個(gè)處理, 這還沒有結(jié)束,我們?cè)陂_頭提到的這個(gè)還沒有解決; MSGpkt = (afIncomingMSGPacket_t *)osal_msg_receive( SampleApp_TaskID );(終于回來了,累啊) 這里涉及到兩個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu): typedef struct
{
void *next;
uint16 len;
byte dest_id;
} osal_msg_hdr_t; typedef struct
{
uint8 event;
uint8 status;
} osal_event_hdr_t; 我查了一下有這么一個(gè)函數(shù)和消息有關(guān)的,如下: *********************************************************************
* @fn osal_msg_send
*
* @brief
*
* This function is called by a task to send a command message to
* another task or processing element. The sending_task field must
* refer to a valid task, since the task ID will be used
* for the response message. This function will also set a message
* ready event in the destination tasks event list.
*這個(gè)函數(shù)主要由任務(wù)調(diào)用發(fā)送一個(gè)命令消息到另一個(gè)任務(wù)或是處理元素,同時(shí)這個(gè)函數(shù)將會(huì)設(shè)定一個(gè)消息事件到目的任務(wù)的事件列表中
*
* @param byte destination task - Send msg to? Task ID
* @param byte *msg_ptr - pointer to new message buffer
* @param byte len - length of data in message
*
* @return ZSUCCESS, INVALID_SENDING_TASK, INVALID_DESTINATION_TASK,
* INVALID_MSG_POINTER, INVALID_LEN
*/
byte osal_msg_send( byte destination_task, byte *msg_ptr )
{
if ( msg_ptr == NULL )
return ( INVALID_MSG_POINTER ); if ( osalFindTask( destination_task ) == NULL )
{
osal_msg_deallocate( msg_ptr );
return ( INVALID_TASK );
} // Check the message header
if ( OSAL_MSG_NEXT( msg_ptr ) != NULL ||
OSAL_MSG_ID( msg_ptr ) != TASK_NO_TASK )
{
osal_msg_deallocate( msg_ptr );
return ( INVALID_MSG_POINTER );
} OSAL_MSG_ID( msg_ptr ) = destination_task; // queue message
osal_msg_enqueue( &osal_qHead, msg_ptr );//入消息隊(duì)列, // Signal the task that a message is waiting
osal_set_event( destination_task, SYS_EVENT_MSG );//設(shè)定一個(gè)系統(tǒng)事件。 return ( ZSUCCESS );
} 看來,這個(gè)osal_msg_send()函數(shù)只是發(fā)送一個(gè)系統(tǒng)事件,而和用戶自定義的事件無(wú)關(guān)(自己猜想的,以后驗(yàn)證。)。 現(xiàn)在大家應(yīng)該豁然開朗了吧,我們終于走到了新的一步了。
| 